Discover the symptoms, health risks, and latest treatment options for atrial fibrillation in Pakistan with expert insights and advanced care solutions.
Atrial Fibrillation in Pakistan: Symptoms & Treatment
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a leading heart rhythm disorder, posing a serious health challenge across Pakistan and globally. Millions are affected, yet many remain unaware of the condition’s potential risks. Recognizing the symptoms of atrial fibrillation, its complications, and exploring the latest treatment options for AFib in Pakistan is crucial for timely and effective care. At Al-Shahbaz Hospital, we are committed to delivering expert cardiac care — helping patients with early diagnosis, personalized management, and ongoing support to improve heart health and overall quality of life.
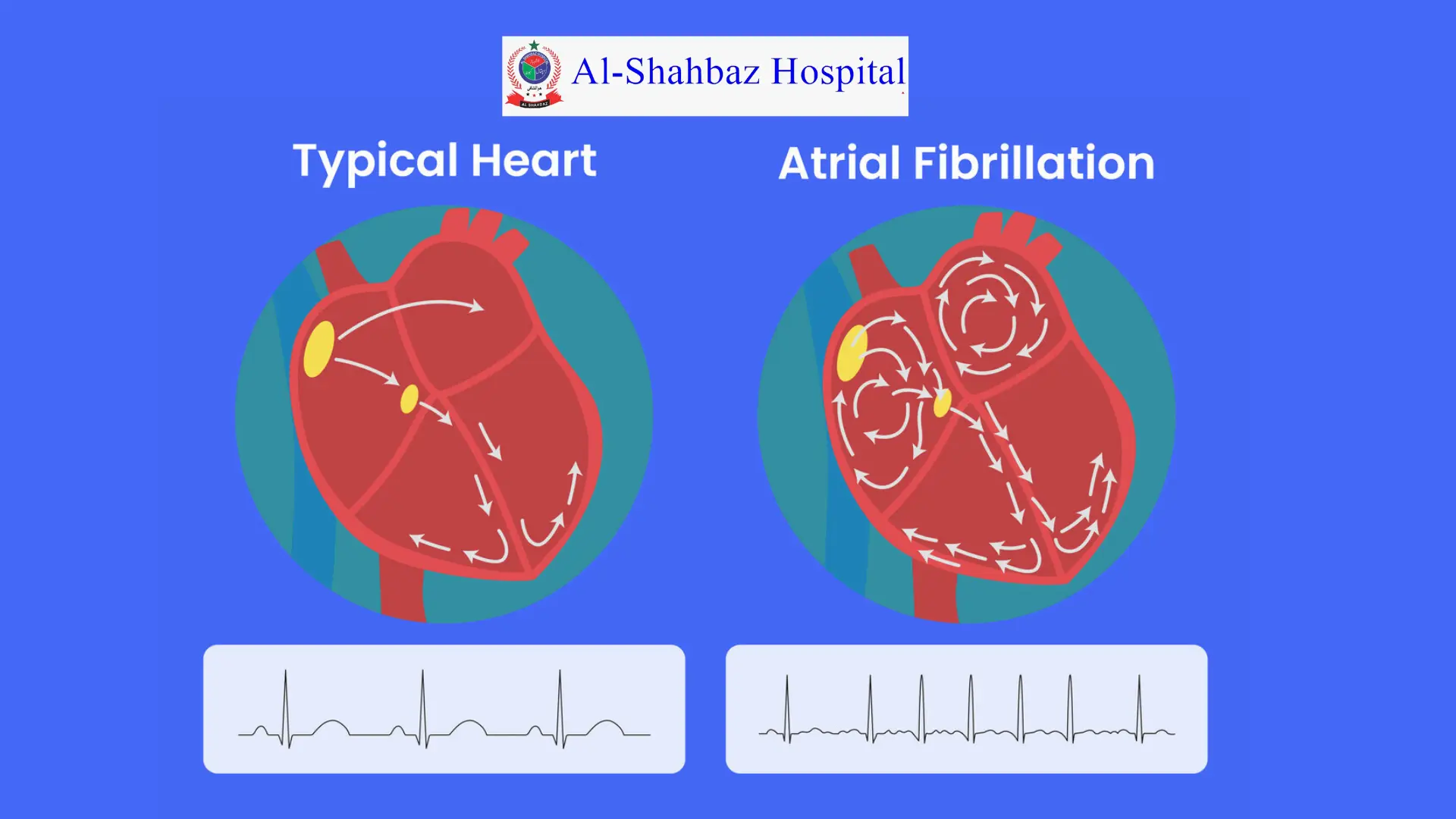
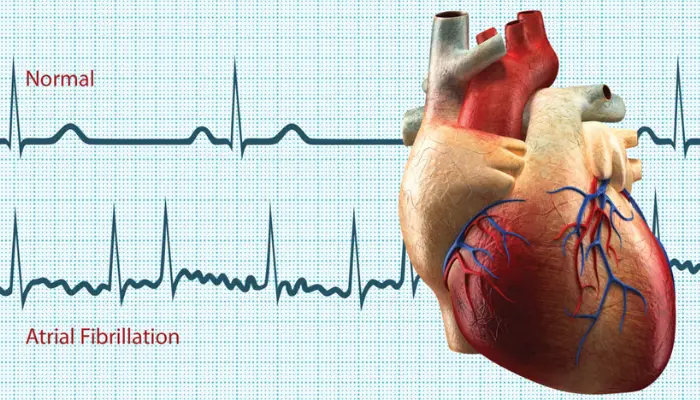
Atrial fibrillation is a condition where the upper chambers (atria) of the heart beat erratically and out of sync with the lower chambers (ventricles). This irregularity can cause blood to pool, increasing the risk of stroke and other complications.
Normal Heart Rhythm:
- Atria contract in a regular, synchronized rhythm to fill the ventricles.
- The ventricles pump blood to the lungs and body.
In Atrial Fibrillation:
- The atria beat chaotically and very fast (up to 300-600 beats per minute).
- The ventricles try to keep up, but their rate remains erratic.
Atrial Fibrillation in Pakistan: Statistics & Insights
Cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death in Pakistan, with heart conditions like atrial fibrillation increasingly being diagnosed.
- Prevalence of AFib: Around 1.8 million people in Pakistan are affected by atrial fibrillation.
- Risk Factors: Hypertension and diabetes are the leading risk factors for AFib, which are prevalent in 32% of the adult population in Pakistan (Pakistan Cardiac Society, 2023).
- Hospital Admissions: Over 10,000 hospital admissions annually in Pakistan are attributed to arrhythmias, with AFib being one of the most common.
According to a study by the International Journal of Cardiology, the incidence of atrial fibrillation in Pakistan has increased by 15% over the last decade, driven by lifestyle changes, aging, and rising healthcare access.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms
Recognizing atrial fibrillation symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. The condition can be particularly deceptive because it may occur without any noticeable signs, yet can result in life-threatening complications if left untreated.
Primary Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation:
• Heart Palpitations: Patients often describe feeling like their heart is “racing,” “fluttering,” or “skipping beats.” This irregular beating pattern is typically the most noticeable symptom.
• Fatigue and Weakness: The inefficient pumping of blood due to irregular heart rhythm can lead to decreased cardiac output, resulting in persistent tiredness and reduced exercise tolerance.
• Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or when lying flat, occurs due to the heart’s reduced ability to pump blood effectively.
• Chest Pain or Discomfort: Some patients experience chest tightness, pressure, or pain, which may be mistaken for other cardiac conditions.
• Dizziness and Lightheadedness: Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause feelings of faintness, dizziness, or near-fainting episodes.
• Reduced Exercise Capacity: Patients often notice a significant decline in their ability to perform physical activities they previously managed easily.
Silent Atrial Fibrillation
One of the most concerning aspects of atrial fibrillation is that it can be completely asymptomatic. Silent AFib affects a significant percentage of patients and is often discovered only during routine medical examinations or when complications such as stroke occur. This underscores the importance of regular cardiovascular screening, particularly for individuals over 65 years of age or those with risk factors.
Major Risks and Complications Associated with Atrial Fibrillation
Understanding the risks associated with atrial fibrillation is essential for appreciating why prompt diagnosis and treatment are so critical. The complications of untreated AFib can be severe and potentially life-threatening.
Stroke Risk
The most serious complication of atrial fibrillation is stroke. AFib increases stroke risk by approximately 5-fold compared to individuals in normal sinus rhythm. The irregular heartbeat allows blood to pool in the atria, forming clots that can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Recent data suggests that AF-related strokes are often more severe and have worse outcomes than strokes from other causes.
Heart Failure
Atrial fibrillation can both cause and worsen heart failure. The irregular, often rapid heart rate prevents the heart from filling and emptying efficiently, leading to reduced cardiac output and eventual heart muscle weakening. Studies show that AFib patients have a significantly increased risk of developing heart failure, and those with existing heart failure face worse outcomes when AFib is present.
Other Cardiovascular Complications
Additional risks include:
• Cardiomyopathy: Prolonged rapid heart rates can lead to weakening of the heart muscle
• Acute coronary syndromes: AFib patients have increased risks of heart attack
• Peripheral embolism: Blood clots can travel to other organs, causing tissue damage
• Quality of life deterioration: Chronic symptoms significantly impact daily functioning
Risk Factors in the Pakistani Population
Research from Pakistani medical centers has identified several key risk factors prevalent in the local population:
• Hypertension: The most common associated condition in Pakistani AFib patients
• Diabetes mellitus: Highly prevalent and closely linked to AFib development
• Coronary artery disease: Significant comorbidity affecting treatment decisions
• Rheumatic heart disease: Still prevalent in Pakistan, contributing to AFib risk
• Age-related factors: Similar to global patterns, with increasing incidence after age 65
Latest Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation
The field of atrial fibrillation treatment has experienced remarkable advances in recent years, offering patients more effective and safer therapeutic options. The latest treatment approaches focus on three main strategies: rate control, rhythm control, and stroke prevention.
Revolutionary Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA)
One of the most significant breakthroughs in AFib treatment is pulsed field ablation, introduced in 2024. This innovative non-thermal ablation technique uses short bursts of high-energy electrical fields called irreversible electroporation to selectively target heart tissue causing atrial fibrillation.
🔬 Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) vs Traditional Ablation – A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) | Traditional Ablation (RF/Cryo) |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue Selectivity | Highly selective (targets only heart tissue) | Less selective, may affect nearby tissues |
| Procedure Time | Shorter duration | Longer procedure |
| Complication Risk | Low (Minimal esophageal/phrenic nerve injury) | Moderate to high |
| Effectiveness | High (Especially in early trials) | Moderate to high |
| Safety Profile | Excellent (Backed by clinical trials) | Acceptable, but more risks involved |
| Recovery Time | Faster recovery | Slower recovery |
✅ Conclusion: PFA offers a breakthrough in atrial fibrillation treatment with improved safety, precision, and efficiency—making it a strong alternative to conventional ablation therapies.
Anticoagulation and Stroke Prevention
Stroke prevention remains a cornerstone of AFib management. The latest guidelines emphasize:
Risk Assessment Tools:
• CHA2DS2-VASc score: Enhanced risk stratification for determining anticoagulation needs
• Individual risk factors: Personalized assessment considering patient-specific factors
Anticoagulation Options:
• Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs): Preferred over warfarin for most patients due to improved safety profiles and convenience
• Novel reversal agents: Development of specific antidotes for DOACs enhances safety
• Left atrial appendage closure: Surgical or percutaneous options for patients unsuitable for long-term anticoagulation
Lifestyle Interventions and Risk Factor Modification
Recent research emphasizes the crucial role of lifestyle modifications in AFib management:
Weight Management: Studies demonstrate that weight loss of 10% or more can significantly reduce AFib burden and improve treatment outcomes.
Exercise Programs: Structured exercise training, when appropriately prescribed, can improve symptoms and quality of life in AFib patients.
Sleep Apnea Treatment: Addressing obstructive sleep apnea through continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy can substantially reduce AFib recurrence.
Alcohol and Caffeine Moderation: Guidelines now provide specific recommendations for alcohol consumption limits and caffeine intake in AFib patients.
Treatment Landscape in Pakistan
The management of atrial fibrillation in Pakistan faces unique challenges and opportunities. Pakistani medical centers are increasingly adopting international guidelines while adapting to local healthcare constraints and patient populations.
Current Treatment Capabilities
Major tertiary care centers in Pakistan now offer:
• Electrophysiology services: Advanced catheter ablation procedures
• Device therapy: Pacemaker and defibrillator implantation
• Anticoagulation clinics: Specialized management of blood-thinning medications
• Multidisciplinary care: Team-based approaches involving cardiologists, electrophysiologists, and specialized nurses..
Challenges and Opportunities
Key considerations for AFib management in Pakistan include:
• Healthcare accessibility: Ensuring rural and underserved populations receive appropriate care
• Cost considerations: Balancing optimal treatment with economic realities
• Training and expertise: Developing local expertise in advanced AFib treatments
• Population-specific research: Conducting studies relevant to the South Asian population.s
Prevention Strategies and Public Health Implications
Prevention of atrial fibrillation requires a comprehensive approach addressing modifiable risk factors at both individual and population levels.

Primary Prevention
Cardiovascular Risk Factor Management:
• Hypertension control: Maintaining blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg
• Diabetes management: Achieving optimal glycemic control
• Cholesterol management: Following current lipid guidelines
• Smoking cessation: Complete tobacco avoidance
Lifestyle Modifications:
• Regular physical activity: 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly
• Healthy diet: Mediterranean-style eating patterns
• Stress management: Techniques to reduce chronic stress
• Adequate sleep: 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly
Secondary Prevention
For patients with established AFib, prevention focuses on:
• Optimizing medical therapy: Ensuring adherence to prescribed medications
• Regular monitoring: Routine follow-up for treatment effectiveness
• Complication prevention: Aggressive stroke and heart failure prevention strategies
• Patient education: Empowering patients to recognize symptoms and seek appropriate care.
Future Directions and Emerging Therapies
The future of atrial fibrillation treatment holds tremendous promise, with several innovative approaches under development.
Technological Advances
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
• Predictive algorithms: AI systems for predicting AFib development and outcomes
• Personalized treatment: Machine learning approaches for optimizing individual treatment plans
• Remote monitoring: Advanced wearable devices for continuous heart rhythm monitoring
Novel Ablation Technologies:
• Robotic ablation systems: Improved precision and outcomes
• Advanced mapping systems: Better identification of AFib sources
• Hybrid procedures: Combining surgical and catheter-based approaches
Pharmacological Innovations
New Anticoagulants: Research continues into safer and more effective anticoagulation options with reduced bleeding risks.
Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Development of more selective medications with fewer side effects and improved efficacy.
Gene Therapy and Regenerative Medicine
Emerging research in genetic approaches to AFib treatment and regenerative therapies for damaged heart tissue shows promising early results.
How Al-Shahbaz Hospital Can Help?
Struggling with Atrial Fibrillation? Expert Care Awaits You

🫀 Take Control of Your Heart Health Today
Don’t let atrial fibrillation disrupt your life. At Al Shahbaz Hospital, our expert cardiologists are here to provide personalized, cutting-edge care using the latest diagnostics and treatment options
✅ Book your consultation now and begin your journey to a healthier heart.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
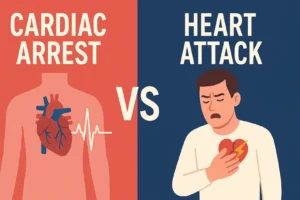
1. What is the difference between atrial fibrillation and a heart attack?
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm disorder affecting the upper chambers of the heart, while a heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked. AFib typically causes palpitations and irregular heartbeat, whereas a heart attack usually presents with chest pain and can be immediately life-threatening. However, AFib can increase the risk of heart attack over time.
2. Can atrial fibrillation be cured completely?
While AFib cannot always be “cured” in the traditional sense, many patients can achieve long-term freedom from symptoms through appropriate treatment. Catheter ablation procedures, particularly newer techniques like pulsed field ablation, can successfully eliminate AFib in 70-90% of carefully selected patients. However, the condition may recur, and ongoing management is often necessary.
3. How common is atrial fibrillation in Pakistan?
Based on recent studies from Pakistani medical centers, AFib affects a significant portion of the elderly population, with patterns similar to global trends. The condition appears to be underdiagnosed in Pakistan, with many cases only discovered when patients present with complications like stroke. The actual prevalence is likely higher than reported due to silent AFib cases.
4. What are the warning signs that require immediate medical attention?
Seek immediate medical care if you experience: sudden onset of severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, fainting or near-fainting, extremely rapid heart rate (over 150 beats per minute), or signs of stroke such as sudden weakness, speech difficulties, or facial drooping.
5. Can lifestyle changes alone manage atrial fibrillation?
While lifestyle modifications are crucial components of AFib management and can significantly reduce symptoms and recurrence, they are typically not sufficient as sole treatment. Most patients require medical therapy, including anticoagulation for stroke prevention. However, lifestyle changes can dramatically improve treatment outcomes and quality of life.
6. How effective is the new pulsed field ablation treatment?
Early clinical studies of pulsed field ablation show very promising results, with success rates comparable to or better than traditional ablation methods. PFA demonstrates excellent safety profiles with reduced complications, particularly lower risks of esophageal injury and phrenic nerve damage. Long-term follow-up data continues to be collected, but initial results are highly encouraging.
7. What is the cost of atrial fibrillation treatment in Pakistan?
Treatment costs vary significantly depending on the specific therapy required. Basic medical management with medications may cost thousands of rupees monthly, while advanced procedures like catheter ablation can cost several hundred thousand rupees. Many tertiary care centers in Pakistan now offer these procedures, and some insurance plans provide coverage for AFib treatment.
8. Can atrial fibrillation cause sudden death?
While AFib itself rarely causes sudden death, it significantly increases the risk of stroke and can contribute to heart failure development. The most dangerous acute complication is stroke, which can be fatal. Additionally, very rapid heart rates in AFib can occasionally lead to hemodynamic compromise, though this is less common than stroke risk.
9. How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed?
AFib is diagnosed primarily through electrocardiogram (ECG) testing, which shows the characteristic irregular heart rhythm. Additional tests may include echocardiography to assess heart structure and function, blood tests to check for underlying conditions, and sometimes longer-term heart rhythm monitoring using Holter monitors or event recorders.
10. Are there any dietary restrictions for atrial fibrillation patients?
Patients on blood-thinning medications like warfarin need to maintain consistent vitamin K intake and may have some dietary restrictions. However, those on newer direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have fewer dietary limitations. Generally, a heart-healthy diet low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is recommended. Alcohol should be limited, as excessive consumption can trigger AFib episodes.